Neurofeedback therapy is gaining popularity as a powerful method to help individuals learn to regulate their brain activity for improved mental and cognitive well-being. However, assessing progress during neurofeedback training is not as straightforward as it may seem. Because the therapy relies on dynamic EEG data, it requires a multifaceted approach that goes beyond simply tracking absolute brainwave values. In this article, we’ll explore how to effectively monitor progress, interpret session results, and evaluate long-term outcomes.
1. Understanding the Limitations of EEG Spectra
One of the first challenges in neurofeedback therapy is dealing with the inherent variability of EEG power spectra. Factors such as emotional state, stress, and external distractions can cause significant fluctuations. Consequently, relying solely on static spectral values is not a reliable way to track progress. Instead, clinicians should:
- Analyze Trends
Focus on changes over time rather than individual session results. - Average Data
Aggregate metrics across sessions to reduce noise and reveal meaningful patterns.
2. Neurofeedback as a Skill of Self-Regulation
Unlike traditional treatments, neurofeedback is about developing the ability to consciously modulate brain activity in response to real-time feedback. The aim is not necessarily to permanently change brainwave patterns at rest but rather to empower individuals to adjust their rhythms when needed.
Through regular practice, participants develop a heightened awareness of their brain state and gain better control over their mental processes, which can translate into improvements in focus, emotional stability, and stress management in daily life.
3. Key Metrics for Tracking Progress
To assess neurofeedback success, it is essential to compare the participant’s EEG activity during training versus rest periods. Key parameters to evaluate include:
- Response Speed
How quickly does the participant reach the target brain rhythm? - Consistency
How well can they maintain the desired frequency range? - Variability
Are fluctuations becoming more stable over time?
Session reports and graphical representations help visualize these metrics and provide valuable insights into the participant’s learning curve.
4. Clinical Improvements and Life Quality Outcomes
The true measure of success in neurofeedback therapy is often reflected in clinical improvements and enhanced quality of life. Potential benefits include:
- Reduced symptoms of conditions like ADHD, anxiety, and insomnia
- Improved cognitive functions such as focus and memory
- Better emotional regulation and stress resilience
Objective assessments using validated scales and patient feedback are essential for capturing these changes. It’s important to remember that significant improvements may require numerous sessions, as progress varies from person to person.
5. The Role of Quantitative Reports
One of the strengths of neurofeedback is its ability to provide objective metrics that quantify training success. Reports generated during each session can track response accuracy, stability,
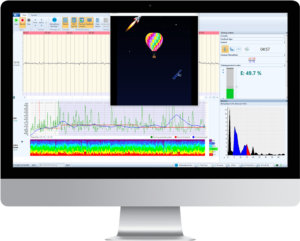
and speed, helping both clinicians and participants monitor progress over time. These reports not only guide therapy adjustments but also motivate participants by visualizing their achievements.
6. Beyond Numbers: Psychological Engagement
While neurofeedback metrics are important, the participant’s psychological experience is equally crucial. Understanding their progress and observing tangible improvements can boost motivation and increase engagement in therapy. Positive reinforcement plays a significant role in maintaining consistency and achieving lasting benefits.
7. Conclusion: A Holistic Approach to Neurofeedback Success
To unlock the full potential of neurofeedback therapy, a holistic approach is essential. Combining quantitative data, clinical assessments, and participant engagement ensures that progress is tracked effectively and meaningful outcomes are achieved. Neurofeedback offers a unique pathway to better self-regulation and cognitive optimization when properly monitored and guided.
A Note on the Effectiveness of Neurofeedback Therapy
Scientific studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of neurofeedback in various applications. For instance:
- Research has shown that neurofeedback can significantly reduce symptoms of ADHD.
- Studies have also reported improvements in anxiety and sleep disorders, with participants experiencing better emotional regulation and stress resilience.
- A meta-analysis published in peer-reviewed journals indicated that neurofeedback can lead to long-term improvements in cognitive functions when used consistently over multiple sessions.
Despite these promising outcomes, neurofeedback therapy is not a quick fix. Significant changes often require a considerable number of sessions, and individual responses may vary. It is most effective when integrated with other therapeutic interventions and lifestyle changes.
If you’re considering neurofeedback therapy, consult with a qualified specialist to understand whether it is suitable for your specific needs and how best to track and evaluate your progress.


